微服务限流简单实现
Table of Contents
一:限流的目的
保障服务稳定的三大利器:熔断、降级、服务限流。今天和大家谈谈限流算法的几种实现方式,本文所说的限流并非是 Nginx、网关层面的限流,而是业务代码中的逻辑限流。
二:限流实现方式
常见的限流算法:固定窗口、滑动窗口、漏桶、令牌桶
https://github.com/lppgo/my_test/tree/master/013_ratelimit%E9%99%90%E6%B5%81
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/L9tP9Wa_UsYzrwllto1naA
1:固定窗口
思想
在一个固定的时间窗口内对请求计数,如果请求数达到阈值那么进行限流,到达时间临界点时重置计数
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| import (
"sync"
"time"
)
type CountLimitRate struct {
duration time.Duration
rate int32
mu sync.Mutex
count int32
lastGetTime time.Time
}
func NewCountLimitRate(duration time.Duration, rate int32) *CountLimitRate {
return &CountLimitRate{
duration: duration,
rate: rate,
lastGetTime: time.Now(),
}
}
func (r *CountLimitRate) Acquire() bool {
r.mu.Lock()
defer r.mu.Unlock()
now := time.Now()
if now.Sub(r.lastGetTime) > r.duration {
r.Reset(now)
}
if r.count >= r.rate {
return false
}
r.count++
return true
}
func (r *CountLimitRate) Reset(getTime time.Time) {
r.lastGetTime = getTime
r.count = 0
}
|
问题
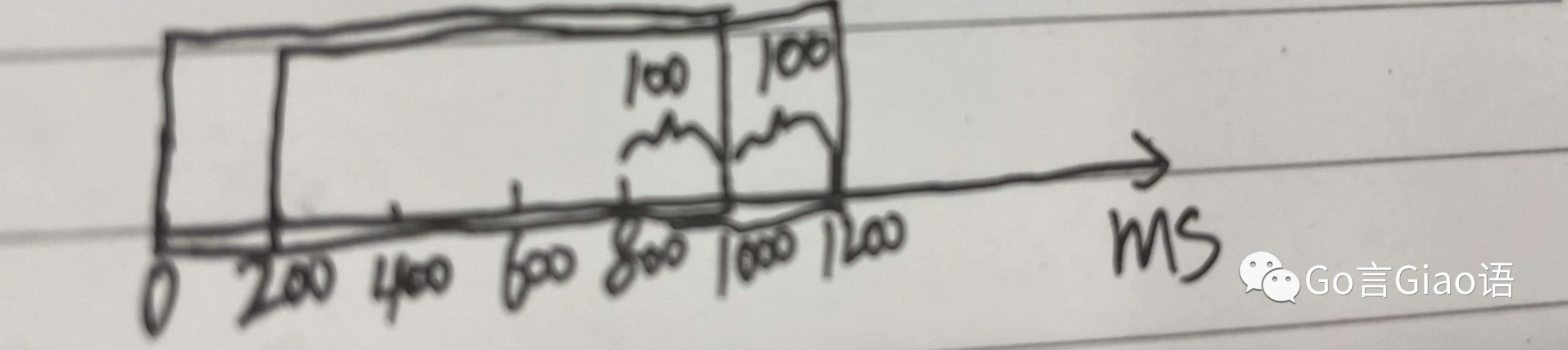
固定窗口会有边界峰值问题即突刺问题
比如窗口大小是 1S,限制是 1S 内最多 100 个请求
前一 S 的最后 200ms 出现 100 个请求,后一 S 的前 200ms 出现 100 个请求,对于固定窗口来说是符合规定的,但此时就出现了边界峰值,1S 内有 200 个请求,可能会压垮后端服务
在这里插入图片描述
2:滑动窗口
思想
滑动窗口算法将一个大的时间窗口分成多个小窗口(timeSlot),每次大窗口向后滑动一个小窗口,并保证大的窗口内流量不会超出最大值,大窗口内的流量是所有小窗口流量之和。
对于滑动时间窗口,我们可以把 1s 的时间窗口划分成 10 个小窗口即窗口有 10 个时间插槽 timeSlot, 每个 timeSlot 统计某个 100ms 的请求数量。每经过 100ms,有一个新的 timeSlot 加入窗口,早于当前时间 1s 的 timeSlot 出窗口,窗口内最多维护 10 个 time slot。
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| import (
"sync"
"time"
)
type timeSlot struct {
startTime time.Time
count int32
}
type SlideWindowLimitRate struct {
rate int32
windowDuration time.Duration
slotDuration time.Duration
mu sync.Mutex
slotList []*timeSlot
}
type SlideWindowDuration struct {
windowDuration time.Duration
slotDuration time.Duration
}
func NewSlideWindowLimitRate(rate int32, slideWindowDuration *SlideWindowDuration) *SlideWindowLimitRate {
return &SlideWindowLimitRate{
rate: rate,
windowDuration: slideWindowDuration.windowDuration,
slotDuration: slideWindowDuration.slotDuration,
slotList: make([]*timeSlot, 0, slideWindowDuration.windowDuration/slideWindowDuration.slotDuration),
}
}
func (r *SlideWindowLimitRate) Acquire() bool {
r.mu.Lock()
defer r.mu.Unlock()
now := time.Now()
discardSlotIdx := -1
for i := range r.slotList {
slot := r.slotList[i]
if slot.startTime.Add(r.slotDuration).After(now) {
break
}
discardSlotIdx = i
}
if discardSlotIdx > -1 {
r.slotList = r.slotList[discardSlotIdx+1:]
}
var reqCount int32 = 0
for i := range r.slotList {
reqCount += r.slotList[i].count
}
if reqCount >= r.rate {
return false
}
if len(r.slotList) > 0 {
r.slotList[len(r.slotList)-1].count++
} else {
r.slotList = append(r.slotList, r.newTimeSlot(now))
}
return true
}
func (r *SlideWindowLimitRate) newTimeSlot(startTime time.Time) *timeSlot {
return &timeSlot{startTime: startTime, count: 1}
}
|
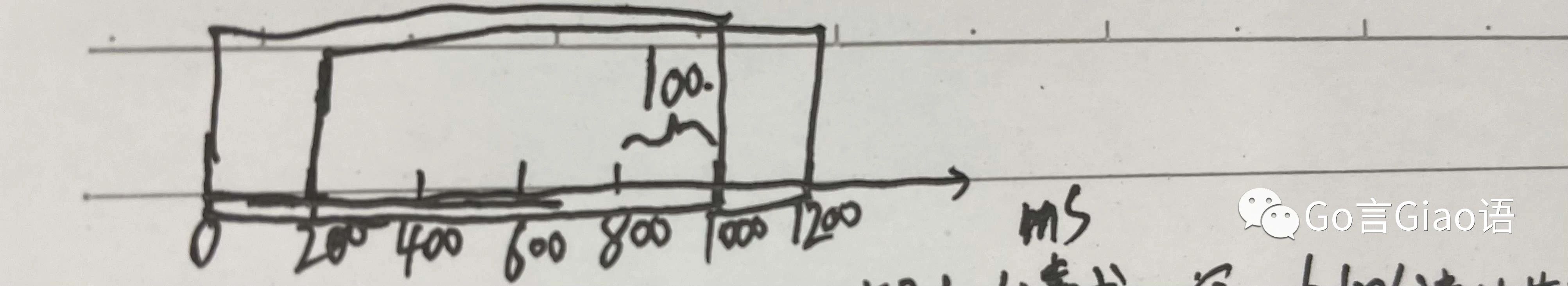
相对于固定窗口的改进
在这里插入图片描述
如上图
前 1 S 的后 200ms 即 8001000ms 来个 100 个请求,窗口内 100 个请求就满了
下 1 S 的前 200ms 即 10001200ms 再来 100 个请求,就会被限流拒绝
3:漏桶
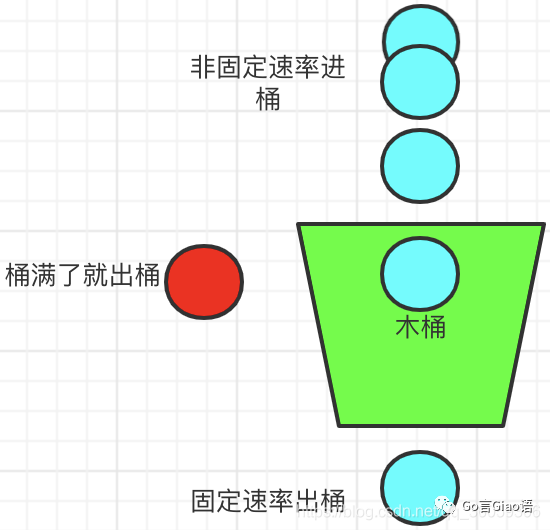
思想
想象有一个木桶,桶的容量是固定的。当有请求到来时先放到木桶中,处理请求的 worker 以固定的速度从木桶中取出请求进行处理。如果木桶已经满了,直接返回请求限流错误。
在这里插入图片描述
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| import (
"math"
"sync"
"time"
)
type LeakBucketLimitRate struct {
rate float64 //每秒速度
capacity float64
mu sync.Mutex
lastLeakTime time.Time
waterCapacity float64
}
func NewLeadBucketLimitRate(rate float64, capacity float64) *LeakBucketLimitRate {
return &LeakBucketLimitRate{
rate: rate,
capacity: capacity,
lastLeakTime: time.Now(),
waterCapacity: 0,
}
}
func (r *LeakBucketLimitRate) Acquire() bool {
r.mu.Lock()
defer r.mu.Unlock()
now := time.Now()
remainWaterCap := math.Max(0, r.waterCapacity-(now.Sub(r.lastLeakTime).Seconds()*r.rate))
r.lastLeakTime = now
if remainWaterCap < r.capacity {
r.waterCapacity = remainWaterCap + 1
return true
}
return false
}
|
适用场景
如果需要以固定的速率处理请求,不接受并发的高流量的请求,那么适合使用漏桶算法
4:令牌桶
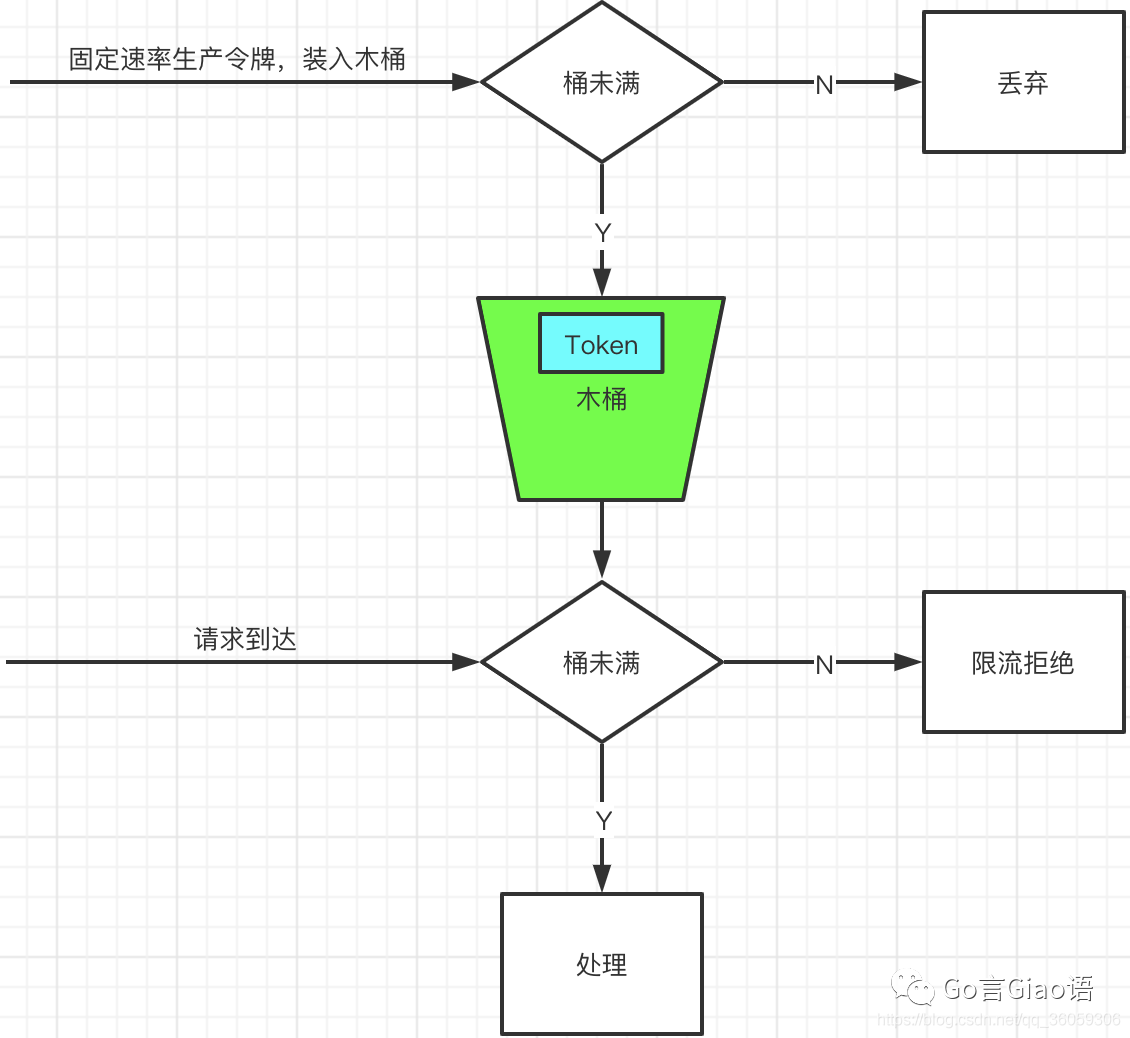
思想
想象有一个木桶,桶的容量是固定的。会以固定的速率往木桶中放入令牌,如果能从木桶中拿到令牌那么允许处理请求,否则返回限流错误。
在这里插入图片描述
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| import (
"math"
"sync"
"time"
)
// 可以使用atomic
type TokenBucketLimitRate struct {
rate float64
capacity float64
mu sync.Mutex
tokenCount float64
lastAddTokenTime time.Time
}
func NewTokenBucketLimitRate(rate float64, capacity float64) *TokenBucketLimitRate {
return &TokenBucketLimitRate{
rate: rate,
capacity: capacity,
tokenCount: 0,
lastAddTokenTime: time.Now(),
}
}
func (r *TokenBucketLimitRate) Acquire() bool {
r.mu.Lock()
defer r.mu.Unlock()
now := time.Now()
addTokenNum := now.Sub(r.lastAddTokenTime).Seconds() * r.rate
r.tokenCount = math.Min(r.capacity, r.tokenCount+addTokenNum)
r.lastAddTokenTime = now
if r.tokenCount > 0 {
r.tokenCount--
return true
}
return false
}
|
适用场景
因为令牌桶可以缓存令牌,所以可以应对突发的高并发流量,比如木桶最多可以存储 500 个令牌,那么就可以最多处理 500 并发量的请求